Other Procedures
Overview, Procedure, Advantages and Risks
Gastrointestinal (GI) Endoscopy
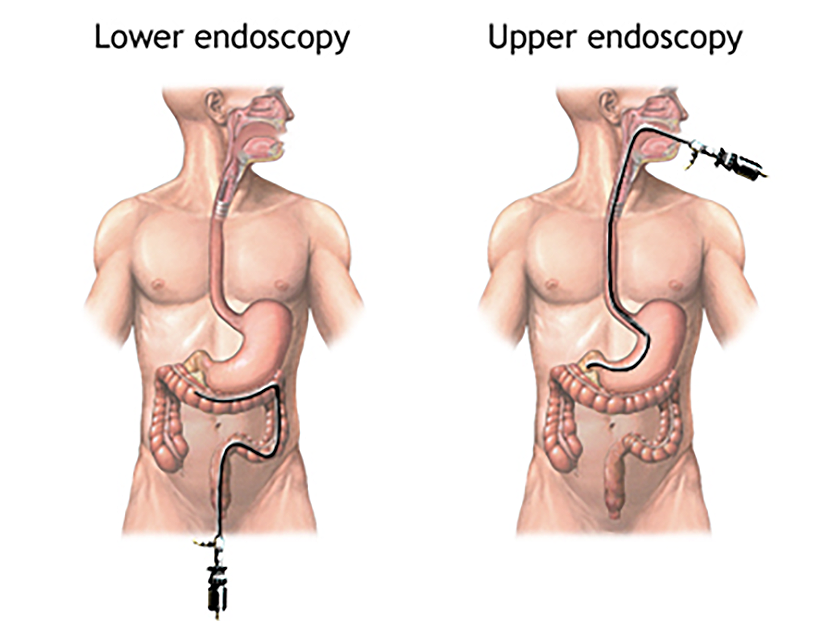
Gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that employs a flexible tube with a camera, known as an endoscope, to visualize the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. Upper GI endoscopy examines the esophagus, stomach, and part of the small intestine, while lower GI endoscopy—also called a colonoscopy—focuses on the colon and rectum.
How the Procedure Works:
Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (EGD):
- Preparation: Patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours before the procedure.
- Sedation: Mild sedation is administered to enhance comfort during the process.
- Insertion: The endoscope is gently inserted through the mouth and navigated down the esophagus into the stomach.
- Examination: The doctor inspects the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine for abnormalities. Biopsies or other procedures may be performed if necessary.
- Completion: The procedure generally lasts about 5-10 minutes. Patients are monitored for a brief period before discharge.
Lower Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (Colonoscopy):
Preparation: A thorough bowel preparation is required, often involving dietary restrictions and laxatives to clear the intestines.
Sedation: Patients receive sedation to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Insertion: The endoscope is inserted into the rectum and advanced through the colon.
Examination: The doctor inspects the colon lining for abnormalities, polyps, or signs of disease. Biopsies can also be taken if needed.
Completion: The procedure usually takes about 15-20 minutes, and patients are closely monitored afterward.
Advantages
Early Diagnosis: Both upper and lower GI endoscopy enable early detection of conditions such as ulcers, cancer, and other gastrointestinal diseases.
Minimally Invasive: These endoscopic procedures are less invasive than traditional surgeries and generally require only mild sedation.
Therapeutic Options: In addition to diagnosis, various therapeutic interventions (e.g., removing polyps, cauterizing bleeding) can be performed during endoscopy.
Quick Recovery: Most patients can resume normal activities shortly after the procedure.
Possible Risks/Cons
Sedation Complications: Risks associated with sedation include breathing difficulties or adverse reactions.
Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding, particularly if biopsies are taken or polyps are removed.
Infection: Though uncommon, there is a risk of infection following the procedures.
Are You a Candidate?
You may be a suitable candidate for upper or lower gastrointestinal endoscopy if you experience:
Symptoms such as unexplained abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, persistent heartburn, changes in bowel habits, or rectal bleeding.
A family history of gastrointestinal issues or colorectal cancer.
Conditions that require closer monitoring, such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Recommendations for the procedure from your healthcare provider based on your health status and symptoms.
Gastrointestinal endoscopy is an essential diagnostic and therapeutic tool for evaluating and treating various GI conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for understanding the need for the procedure and any associated risks.
Get more information about our weight loss surgery packages.
Request a Free Quote
Your path to a healthier life begins here. Trust in us to support you as you take these empowering steps towards your health and happiness.
Our Procedures
Contact Us
- Plaza 307 Paseo Colón 1622 suite 1, Col. Madero C.P. 88270 Nuevo Laredo, Tamps.
- ceballosdoctors@gmail.com
- +52 867 117 1998